
Run MongoDB in Docker
A main strength of MongoDB is arguably its ease-of-use. You can complete its installation and have your first database up-and-running in minutes. With docker, this process can become even easier. In this post, we’ll install and create a MongoDB database in a docker container in just a few simple commands. All you need to get started is an installation of docker. The commands in this post assume that you’re running Ubuntu, but this commands will work fine with most linux distros.
MongoDB container image
MongoDB conveniently provides us with an official container. To try it out:
$ mkdir ~/data
$ sudo docker run -d -p 27017:27017 --name mongo -v ~/data:/data/db mongo
Let’s explain the syntax of the docker run command. The first command is to create a ~/data directory where the data from the container will be stored on the host.
The docker run is used to run a container, the -d flag is to run in a detached mode i.e. in the background, -p flags publishes the port 27017 exposed on the container on port 27017 on the docker host, --name mongo attaches the name mongo to the running container instead of a generated hash key.
-v ~/data:/data/db provides the volume path on the docker host to persist the data from the container. Lastly the mongo at the end is the name of the image to run.
If you run this command, the docker firstchecks if there is a mongo image locally, if one exists it runs it else it will pull one from the DockerHub Registery and then run it. At this point, you should have a MongoDB instance listening on port 27017 and its data is stored in ~/data directory of the docker host.
Connecting to your MongoDB container
# Install the MongoDB client
$ sudo apt-get install mongodb-clients
# Change mydb to the name of your DB
$ mongo localhost/testdb
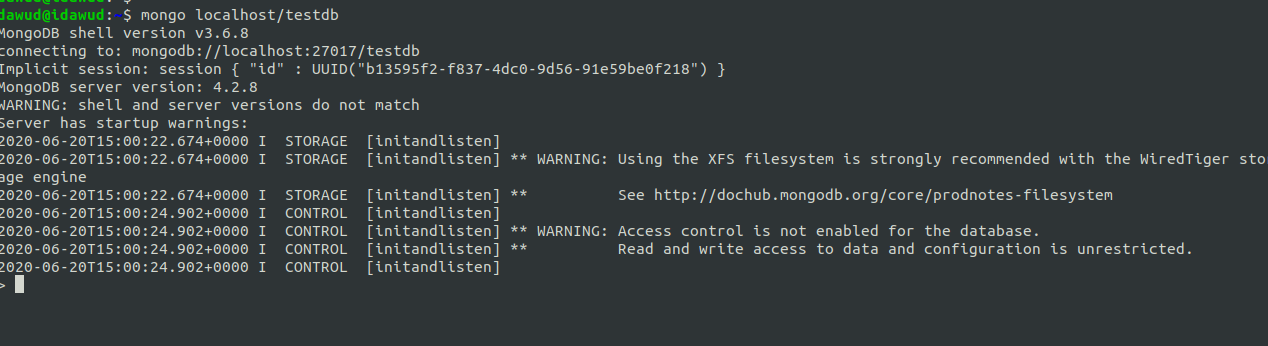
After that, you’ll get into a MongoDB prompt, like this:
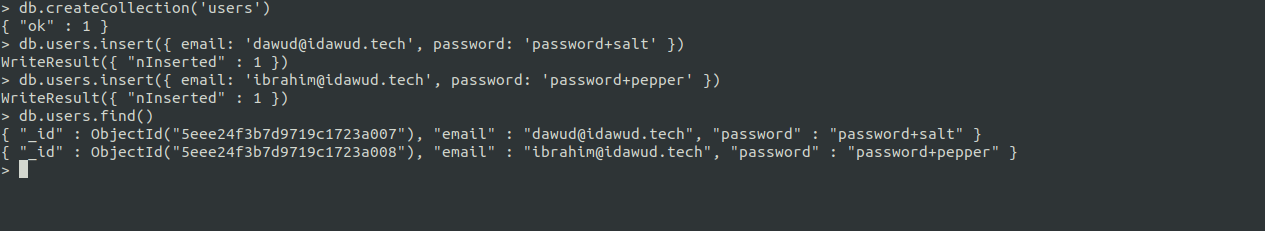
We want to store some users in our database:
db.createCollection('users')
db.users.insert({ email: 'dawud@idawud.tech', password: 'password+salt' })
db.users.insert({ email: 'ibrahim@idawud.tech', password: 'password+pepper' })
db.users.find()
You should see the entries that you created:
Stopping your MongoDB container
Because we already gave our container a name, It’s simple as running sudo docker stop mongo to stop the running docker container.